Machine Setup for Computational Music
This coming summer I’m leading a summer camp on digital music and sound generation. There are many steps to get the computers set up, and I record them here to share with helpful system administrators and my future self.
Software to Install
The following is a list of the base software that needs to be installed:
- Pure Data: an open-licensed flow-based programming environment. There are a few distributions available, but we want Miller Puckette’s vanilla distribution.
- Arduino IDE: an open-licensed development environment for the Arduino platform. We use the standalone desktop IDE. There’s a web client that may be nice to use someday, but I want to be able to work offline.
- VMPK: an open-licensed virtual MIDI controller, which serves as a bridge between Pure Data and the system audio. (PureData generates MIDI commands, but it doesn’t play MIDI notes.)
- Sonic Pi: an open-licensed music synthesis environment based on the Ruby programming language.
Configuration and Testing
Once the software is installed, some of it needs to be configured and all of it should be tested. The following steps should be followed in order.
macOS
The operating itself needs to be set up to allow MIDI commands to pass between applications. The following steps create a bridge for inter-application communication (IAC):
- Ensure that VMPK and Pure Data are not open.
- Hit
Command-Spaceand enter Audio MIDI Setup. - Click Window / Show MIDI Studio.
- Double-click IAC Driver.
- Toggle Device is online on.
- In Ports, ensure at least one port is available. Add one if necessary. The name of the port isn’t important.
- Quit Audio MIDI Setup. It doesn’t need to remain open.
VMPK
We set up VMPK to receive MIDI commands with the following steps:
- Open Virtual MIDI Piano Keyboard.
- Click Edit / MIDI Connections
- Check Show Advanced Connections.
- Set MIDI IN Driver to CoreMIDI.
- Set Input MIDI Connection to IAC Driver Bus 1—or whatever you named the port earlier.
Pure Data
We set up Pure Data to send MIDI commands with the following steps:
- Open Pure Data.
- Click Media / MIDI Settings.
- Click the button under Output Devices, select VMPK Input, and hit OK.
We test whether the IAC bridge is working by programming a Pure Data patch to issue MIDI commands:
- Download the patch test_midi.pd.
- Open the patch in Pure Data. It should look like this:
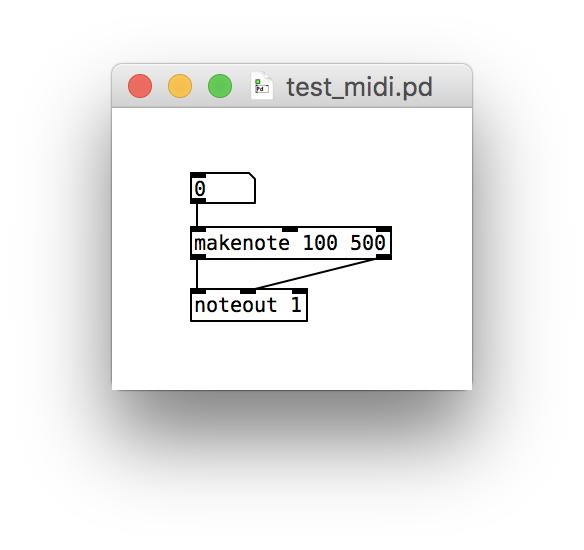
- Drag on the number box in your patch to hear a slur of notes triggered by Pure Data and played by VMPK.
Additionally, we need a couple of helper packages to make writing patches easier:
- Install the zexy package, which makes talking to Arduino over the serial port a bit easier. The easiest way to install it is through builtin package manager. Access it via Help / Find Externals, search for zexy, and install the most recent version. If you are a system administrator, it might be easier to mass install it by downloading the source and extracting it to the right directory.
- Test the zexy installation with the patch test_zexy.pd: Click on the top message containing a list of letters to run the patch. If the installation has worked, zexy’s
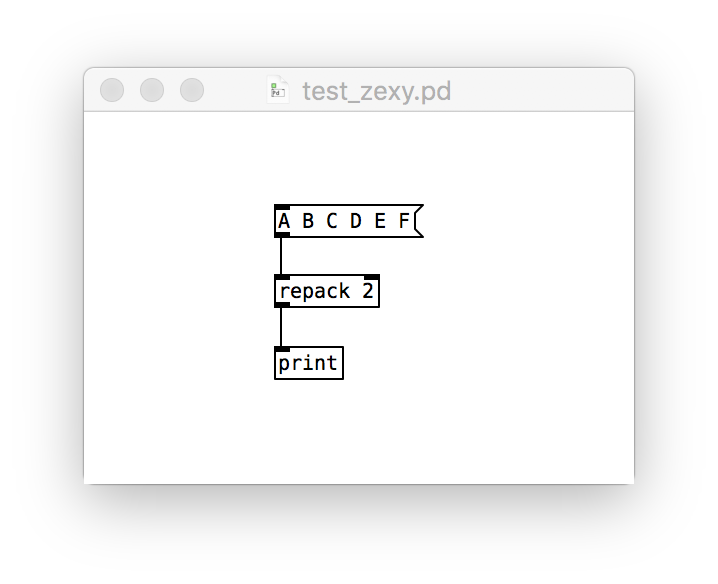
repackcommand will parcel the list into 2-tuples, which you’ll see printed in Pure Data’s console window like this:print: list A B print: list C D print: list E F
- Install the comport package in the same manner as zexy.
- Test the comport installation with the patch test_comport.pd: Click on the
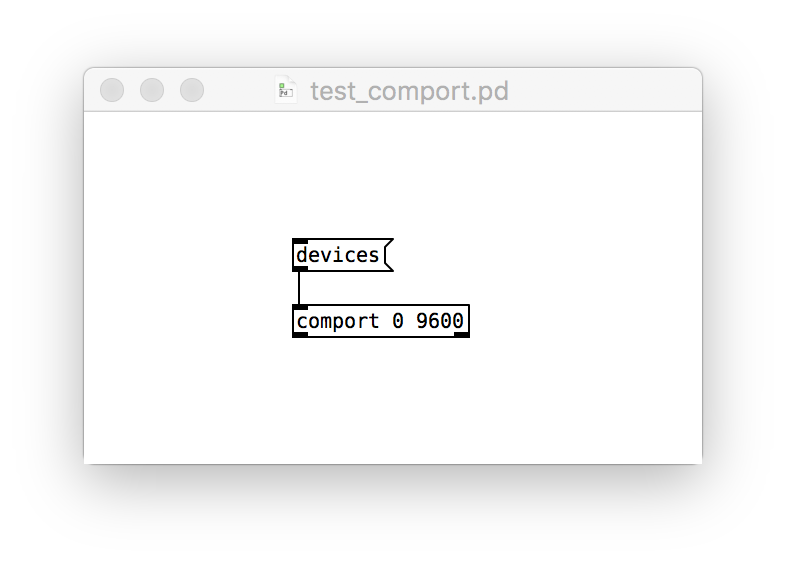
devicesmessage to see a list of available serial ports. It may take a few seconds to run. The list will likely be quite boring unless you have an Arduino board plugged in.
Arduino
The Arduino boards that we use are Adafruit Metros. Unlike official Arduinos, the Metros contain an FTDI chip and serial port hardware that require special drivers on macOS. Adafruit provides some instructions, but in short, we need these two driver packages installed:
- The most recent driver from FTDI for macOS x64
- The most recent USB to UART driver for Silicon Labs for macOS
Beyond have an Adafruit Metro on hand, I don’t know of an easy way to test whether these drivers installed correctly.
Sonic Pi
Sonic Pi should work properly out of the box. Run this code from the examples to test it:
live_loop :haunted do
sample :perc_bell, rate: rrand(-1.5, 1.5)
sleep rrand(0.1, 2)
end